99. Recover Binary Search Tree
You are given the root of a binary search tree (BST), where the values of exactly two nodes of the tree were swapped by mistake. Recover the tree without changing its structure.
Example 1:
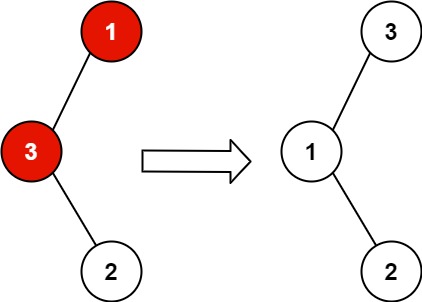
Input: root = [1,3,null,null,2] Output: [3,1,null,null,2] Explanation: 3 cannot be a left child of 1 because 3 > 1. Swapping 1 and 3 makes the BST valid.
Example 2:
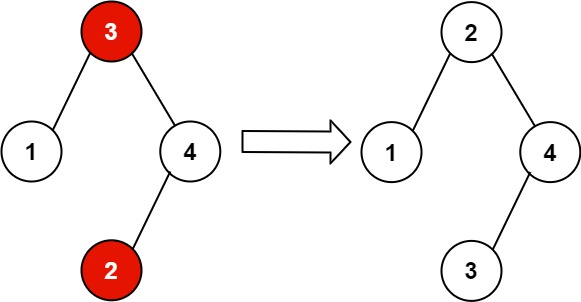
Input: root = [3,1,4,null,null,2] Output: [2,1,4,null,null,3] Explanation: 2 cannot be in the right subtree of 3 because 2 < 3. Swapping 2 and 3 makes the BST valid.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[2, 1000]. -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
The solution to the above question is-
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* f=NULL;
TreeNode* s=NULL;
TreeNode* prev=new TreeNode (INT_MIN);
void inorder(TreeNode* root){
if(root==NULL)return;
inorder(root->left);
if(f==NULL && prev->val>root->val)f=prev;
if(f!=NULL && prev->val > root->val)s=root;
prev=root;
inorder(root->right);
}
void recoverTree(TreeNode* root) {
inorder(root);
swap(f->val,s->val);
}
};

0 Comments
If you have any doubts/suggestion/any query or want to improve this article, you can comment down below and let me know. Will reply to you soon.